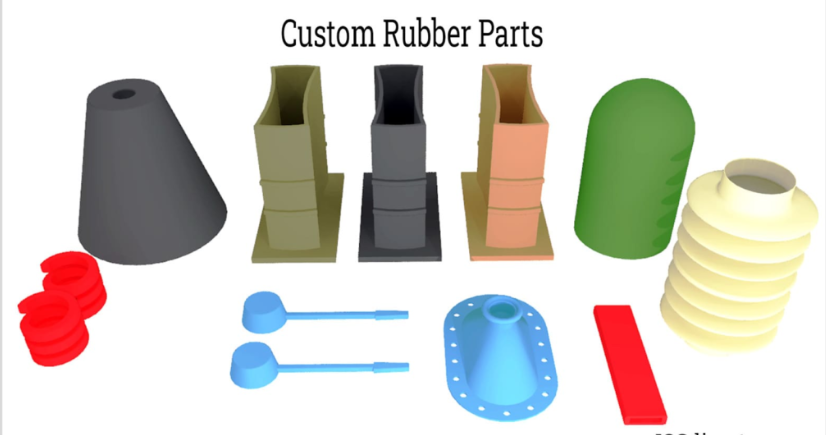
6 Steps Involved in a Custom Rubber Molding Project
Custom rubber molding services can create components and products using different methods and steps. These components are created to meet the specific needs of different products in various industries. Here are the six steps involved in a custom molding project.
Understanding Design Specifications
Understand design specifications, such as dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements. This allows the engineer to select the right rubber compounds and molding techniques to match your project needs. It also allows partners to review CAD drawings and prototypes or samples that can help guide decision-making, from material selection to tooling design to post-processing methods.
Identifying Rubber Materials
Selecting rubber materials involves choosing the correct base polymers, additives, and curing agents to help achieve the desired durability, elasticity, and resistance properties. This information informs chemical composition recommendations for best performance. Once you know the materials needed for a component, you can determine whether it is right for the project.
Crafting Rubber Molds
After finalizing product designs and approving rubber compounds, fabricators will then craft molds. Mold manufacturers construct specialized tools for custom products using machining, EDM, or 3D printing. Engineers analyze factors like polymer flow to optimize mold surface finishes, vent placement, undercuts, textures, and split lines. In some cases, they may create one master mold that supports multiple cavity configurations.
To create the component, operators fill the mold cavities with rubber compounds, apply heat and pressure, and cool the molds. For rubber molding injection, they inject preheated rubber into the molds: rubber compression molding and rubber extrusion, using hydraulic presses to create shapes. Experts align molding processes with tooling designs and material specifications to create the necessary tool.
Cooling and Curing
Once the desired shape is formed, manufacturers allow adequate cooling and curing. This strengthens the rubber’s cross-linking and bonding. They may use advanced techniques, such as active cooling with nitrogen or carbon dioxide. Mold designs may also support proper thermal transfer. Controlled cooling and curing help prevent defects like shrinkage or warpage.
Conducting Quality Control
Quality control involves inspecting sample parts from each batch. Fabricators should check dimensions and also test physical and chemical properties. They compare the data to the specifications of end-use applications to determine success. Testing allows them to confirm that batches meet requirements before full production. Operators may inspect tooling and equipment. Quality control helps ensure that the finished parts will maintain consistent, high performance.
Prototyping created parts allows testing and analysis under real-world conditions specific to the job. The results enable manufacturers to refine large production runs. Once the product has been prototyped, they are used as the benchmark for the entire project.
Finishing and post-processing
After the product is finished, it requires deflating, cleaning mold release, coating rubber, and preparing parts for shipping. Fabricators can apply specialized coatings that bond with the rubber for desired surface properties. This integration maintains quality and eliminates the potential for defects.
Start Your Custom Rubber Molding Project Today
Experts have the required people, processes, machinery, and experience to handle any of your projects. Reach out for support so you can focus most of your resources on developing your core capabilities and gain access to advanced materials science, tooling, and precision equipment. Partner with an experienced rubber molding partner today for your industrial components.